In real plant conditions, pumps don’t fail suddenly. They fail slowly due to wear and corrosion. Most buyers ask on Google: Why do metal pumps fail early? or How to reduce pump downtime? Industry data shows over 60% of pump breakdowns link to wear & corrosion degradation. This directly causes metal pump lifespan reduction and rising energy costs. Poor material choice increases the effects of wear and corrosion, especially in chemicals and slurry handling. Smart buyers focus on wear and corrosion resistance, proper coatings, and pump maintenance for wear and corrosion. The right alloys and proven solutions for pump wear problems help reduce corrosion in pumps and protect long-term ROI.
What Mechanical Wear Is And How It Develops In Metal Pumps:
- Wear & corrosion mean metal parts slowly get damaged while working
- Pump parts rub each other again and again
- Dirty water or chemicals scratch the metal
- Heat makes metal weak and thin
- Effects of wear and corrosion include leaks and noise
- Pump shakes more than normal
- Parts lose shape and strength
- Metal pump lifespan reduction happens faster
- No oil or grease increases damage
- No pump maintenance for wear and corrosion makes failure sudden
- Low wear & corrosion resistance breaks pumps early
How Wear and Corrosion Silently Destroy Industrial Pumps:
| Time Period | What Happens Inside the Pump | Impact |
| 0–3 Months | Micro scratches and early corrosion pits | No visible issue |
| 3–6 Months | Clearance increases, surface roughness | Flow drops |
| 6–9 Months | Seal and bearing stress | Noise & vibration |
| 9–12 Months | Cracks, leaks, wall thinning | Sudden failure |
Key Causes of Wear in Industrial Pump Systems:
- Any kind of dirty liquid enters the pump
- Pump runs without liquid (dry running)
- Air bubbles hit metal parts
- Wrong pump speed causes stress
- Parts not fitted straight
- Weak metal quality used
- No wear & corrosion and their prevention planning
- No coating to reduce corrosion in pump
- Not using best materials for wear and corrosion resistance
- Ignoring early damage signs
- Leads to costly solutions for pump wear problems later
Critical Differences Between Wear, Corrosion, Erosion, and Cavitation That Most Plants Ignore:
Many pump failures are blamed on corrosion alone, but multiple forces act together. Each type of damage behaves differently.
| Damage Type | What It Means | Common Cause |
| Wear | Metal rubbing metal | Poor alignment, dry running |
| Corrosion | Chemical reaction | Acids, moisture, heat |
| Erosion | Surface cutting | Slurry, sand, high velocity |
| Cavitation | Bubble collapse | Low suction pressure |
All these together cause wear and corrosion degradation and reduce pump life.
What is Corrosion & How Chemical Reactions Damage Metal Pumps:
Corrosion is like rust eating a bicycle left in rain. Inside pumps, chemicals react with metal and slowly chew it away. This wear & corrosion weakens walls, cracks joints, and causes leaks. Think of salt spoiling tools. This is wear and corrosion degradation. Over time, this leads to metal pump lifespan reduction. Water, acids, and heat speed this damage. The effects of wear and corrosion include low flow, noise, and breakdowns. Without pump maintenance for wear and corrosion, repair costs rise. Using coatings and plastics are solutions for pump wear problems that help reduce corrosion in pumps and avoid failures.
How Wear and Corrosion Affect Pumps in Different Industrial Applications:
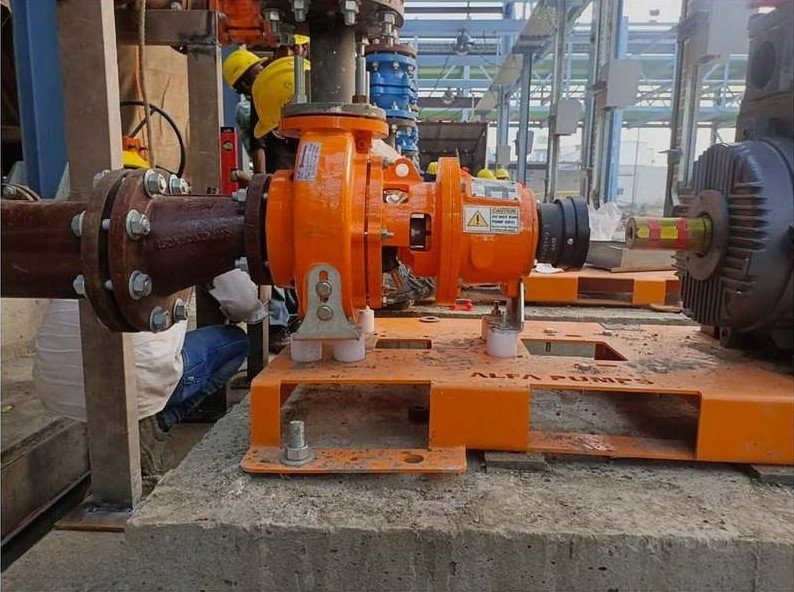

Different industries face different operating conditions. One pump design cannot suit all applications.
- Chemical Processing Plants – Continuous chemical exposure causes fast corrosion. Poor material selection increases surface damage and leakage risk.
- Textile and Dye Industry – Dyes combined with fibres cause abrasion and chemical attack together, leading to rapid wear.
- Pharmaceutical Industry – Even small corrosion pits can cause contamination. Surface smoothness and material purity are critical.
- ETP and STP Plants – Slurry erosion combined with biological corrosion causes severe wear on metal pumps.
Choosing application-specific pumps improves wear and corrosion resistance and reliability.
Key Causes of Corrosion in Pump Applications:
These are somewhat similar to how corrosion also happens:
- Poor material choice causes wear & corrosion, leading to early surface damage.
- Dirty fluids increase wear & corrosion degradation inside pump passages.
- High temperature speeds chemical attack, reducing wear & corrosion resistance.
- Wrong sealing allows air entry, accelerating rust and metal pump lifespan reduction.
- Poor lubrication increases friction, a key factor in effects of wear and corrosion.
- No routine checks ignore pump maintenance for wear and corrosion needs. This demands solutions for pump wear problems.
Read Also: Future of Fluid Handling in India – Insights from Alfa’s Global Expertise
Hidden Operating Costs Caused by Wear and Corrosion in Pumps:
Wear & corrosion damage is not limited to pump parts. It increases overall plant expenses without warning. Many plants replace pumps but never calculate how much money was lost before replacement.
Major hidden costs include:
- Higher electricity consumption due to worn impellers
- Frequent spare replacement and labor cost
- Emergency breakdown repairs
- Production loss during downtime
- Safety risk due to leakage
Pumps with low wear & corrosion resistance may look cheaper at purchase, but they cost more during operation.
Read Also: Cost Savings with Non-Metallic Pumps vs Metal (Titanium) Pumps
How Wear and Corrosion Accelerate Pump Failure:
Suppose you have a metal water tap at home. First, external corrosive water makes it rust on the outside. Simultaneously, the same water will damage it on the inside. Right?
The same happens in pumps. Wear and corrosion act like a double attack. Flowing liquid rubs pump parts, causing wear & corrosion degradation. At the same time, chemicals or water cause rust, leading to effects of wear and corrosion. This speeds up cracks, leaks and noise. The result is metal pump lifespan reduction. Without proper pump maintenance for wear and corrosion, breakdowns come early. Using the best materials for wear and corrosion resistance and smart solutions for pump wear problems helps reduce corrosion in pumps and saves money.
Early Warning Signs of Wear and Corrosion Damage in Pumps:
Wear & corrosion give early signals, but they are often ignored.
Common warning signs:
- Reduced flow without process change
- Increased motor current and power consumption
- Seal leakage stains near casing
- Abnormal vibration or noise
- Repeated bearing failures
These are clear effects of wear and corrosion. Early pump maintenance for wear and corrosion avoids emergency shutdown.
How Wear And Corrosion Affect Efficiency, Maintenance And Downtime:
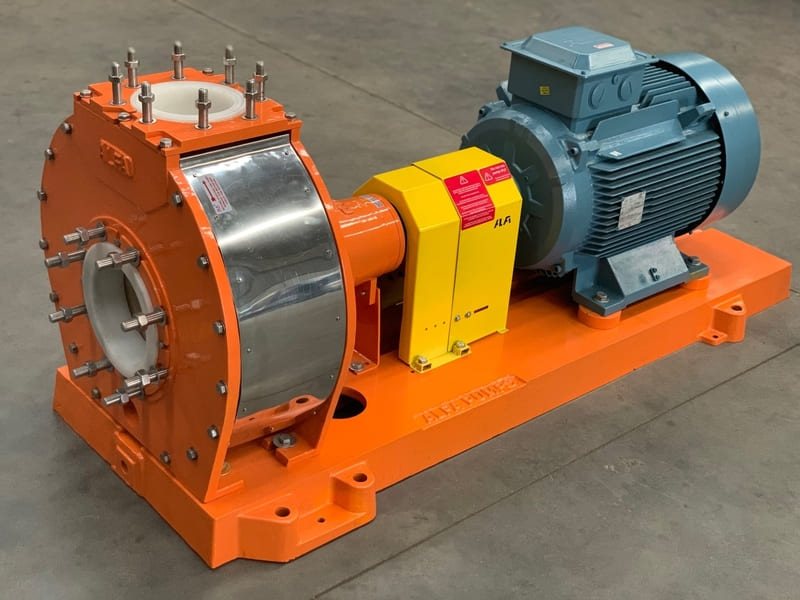

Wear means parts slowly rub away. Wear & corrosion happen when water, chemicals, and sand keep hitting pump parts daily. This causes wear & corrosion degradation. Flow becomes weak. Power use increases. Output drops. These are clear effects of wear and corrosion.
Metal parts thin out. This leads to metal pump lifespan reduction. Pumps break early. Frequent repairs follow. This raises pump maintenance for wear and corrosion costs. Seals leak. Shafts shake. Bearings fail. Work stops suddenly. Downtime hurts production. Wear & corrosion resistance is missing in poor pumps. Factories lose time. Workers wait. Money drains fast.
Why Pump Material Selection is Critical for Wear and Corrosion Resistance:
Pump shape alone cannot protect against wear & corrosion. Material plays a bigger role.
Metal Materials:
- React with chemicals
- Develop rust and pitting
- Lose thickness over time
Advanced Non-metallic Materials:
- Do not rust
- Resist chemical attack
- Have smooth surfaces reducing friction
- Provide stable wear and corrosion resistance
This is why modern solutions for pump wear problems focus on engineered materials.
Real Industrial Pump Failure Examples Caused by Wear and Corrosion:
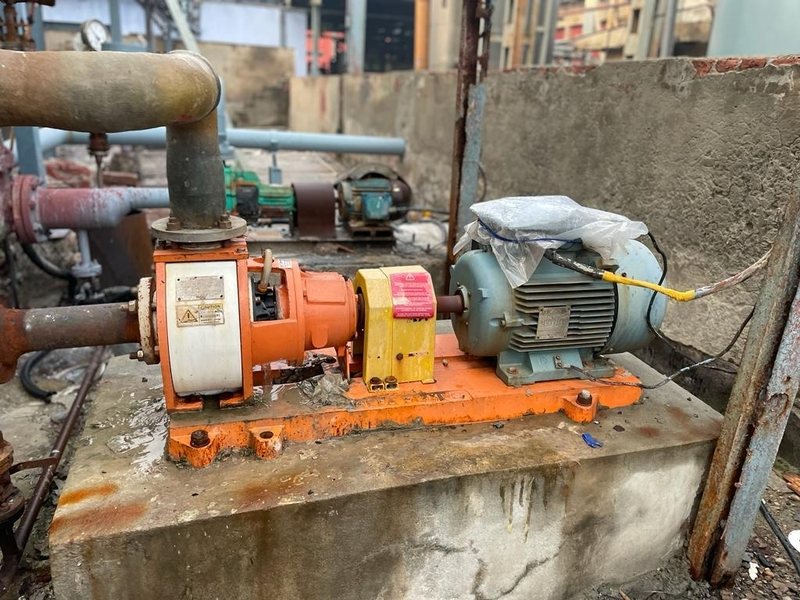

In many chemical plants, metal pumps fail within 8–12 months due to corrosion and wear. Maintenance teams replace seals, bearings, and impellers repeatedly. Energy consumption keeps increasing.
After switching to corrosion-resistant non-metallic pumps:
- Pump life increases
- Maintenance frequency reduces
- Downtime reduces
- Energy efficiency improves
This clearly shows how wear and corrosion resistance protect long-term ROI.
Read Also: Non-Metallic Pumps for Corrosive Chemicals A Buyer’s Guide
Methods to Reduce Wear and Corrosion and Extend Pump Lifespan:
- Start by choosing the best materials for wear and corrosion resistance. These are simple solutions for pump wear problems.
- Non-metallic or coated parts help reduce corrosion in pumps. Smooth flow paths lower damage.
- Proper alignment avoids rubbing.
- Clean fluids reduce grit damage.
- Regular checks prevent surprises.
- Timely part replacement controls wear & corrosion and their prevention.
- Use pumps designed for chemicals and slurry like we provide at Alfa Pumps
- Strong casing improves wear and corrosion resistance.
- Right speed reduces stress.
Alfa Pumps design focuses on wear or corrosion control. We are sharing below how and why should you connect with us for the best corrosion resistance pumps…..
Why Choose Alfa Pumps – Built-in Wear and Corrosion Resistance in Global Standards
- Alfa Pumps’ chemical process pumps are engineered to resist corrosion in extreme conditions for long service life.
- Our NK and NKP Series use premium thermoplastics like PVDF and PFA. In simple words, these deliver high corrosion resistance and handle aggressive chemicals safely.
- Alfa Pumps’ non-metallic pumps are designed to reduce wear & corrosion degradation compared to metal pumps. This ensures lowering lifecycle costs and maintenance needs.
- The company has delivered over 42,000 pumps globally. We have a consistent focus on pump maintenance for wear & corrosion performance and reliability.
- Our lineup includes modular designs. It makes servicing easier, addressing solutions for pump wear problems and improving uptime.
- Alfa Pumps emphasizes customised engineering. So each pump resists wear & corrosion specific to the process fluid and environment.
Final Insight on Pump Wear and Corrosion Control:
In India, over 30% industrial pump failures happen due to wear & corrosion. This causes high downtime losses yearly. Alfa Pumps use the best materials for wear and corrosion resistance. Delay means higher repair bills and sudden shutdowns. Choose Alfa Pumps now to Avoid metal pump lifespan reduction – Protect uptime – Secure profits.
FAQs:
Corrosion causes pitting and uneven surface loss. This internal shape distortion due to corrosion in pumps affects flow balance, increases vibration, and stresses rotating parts.
As wear increases, clearances grow and internal leakage rises. This efficiency loss due to worn pump internals causes reduced output and higher power consumption.
Heat speeds up chemical reactions and weakens metal hardness. This temperature-accelerated wear and corrosion in pumps causes faster internal breakdown.
Slurry, sand, or solid particles hit internal parts repeatedly. This leads to abrasive wear damage inside pump flow paths, removing material layer by layer.
Early signs include vibration, noise, flow drop, and seal leakage. These indicate early-stage wear and corrosion damage inside pumps and should be addressed quickly.
Metal reacts with chemicals and also suffers surface loss due to movement. This continuous wear and corrosion action in metal pumps reduces strength and leads to premature shutdown.

Mr. Sanket Patel is a visionary industrial leader and managing director of Alfa Pumps. He leads the company’s innovation in fluid handling solutions, focusing on chemical process pumps designed for corrosive fluids.




